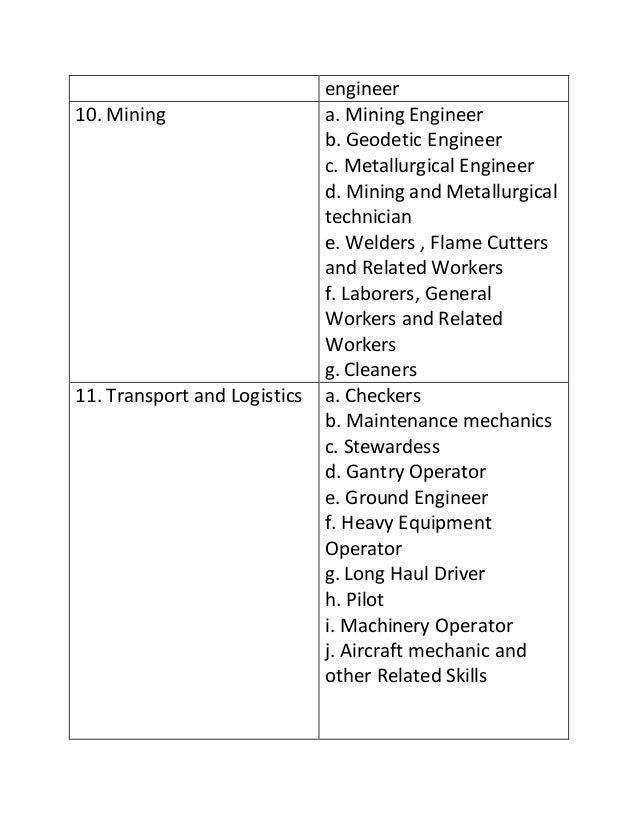
- Key Employment Generators Esp 9 Driver
- Key Employment Generators Esp 9 Repair
- Key Employment Generators Esp
Teaching skills can be adapted for the teaching of English for Specific Purposes. Moreover, she will need to look for content specialists for help in designing appropriate lessons in the subject matter field she is teaching. As an ESP teacher, you must play many roles. You may be asked to organize courses, to set.
- Audio Asylum - Search of All Forums - Enter your search criteria. Click here for tips on using our search.
- May 19, 2018 EsP 9-Modyul 16 30,353 views. Share; Like; Download. Rivera Arnel, Teacher at BNHS-VMA, LPU. Bokasyonal o negosyo na kasama sa tinatawag na Key Employment Generators ( KEG) ay tugma sa iyong minimithi at sa mga personal o mga pansariling salik tulad ng mga hilig o interes, kakayahan, pagpapahalaga at kasanayan.
Key Employment Generators Esp 9 Driver
Key generators are constructed using one of the getInstance class methods of this class.
Key Employment Generators Esp 9 Repair
KeyGenerator objects are reusable, i.e., after a key has been generated, the same KeyGenerator object can be re-used to generate further keys.
There are two ways to generate a key: in an algorithm-independent manner, and in an algorithm-specific manner. The only difference between the two is the initialization of the object:
- Algorithm-Independent Initialization
All key generators share the concepts of a keysize and a source of randomness. There is an
initmethod in this KeyGenerator class that takes these two universally shared types of arguments. There is also one that takes just akeysizeargument, and uses the SecureRandom implementation of the highest-priority installed provider as the source of randomness (or a system-provided source of randomness if none of the installed providers supply a SecureRandom implementation), and one that takes just a source of randomness.Since no other parameters are specified when you call the above algorithm-independent
initmethods, it is up to the provider what to do about the algorithm-specific parameters (if any) to be associated with each of the keys. - Algorithm-Specific Initialization
For situations where a set of algorithm-specific parameters already exists, there are two
initmethods that have anAlgorithmParameterSpecargument. One also has aSecureRandomargument, while the other uses the SecureRandom implementation of the highest-priority installed provider as the source of randomness (or a system-provided source of randomness if none of the installed providers supply a SecureRandom implementation).
In case the client does not explicitly initialize the KeyGenerator (via a call to an init method), each provider must supply (and document) a default initialization.
Every implementation of the Java platform is required to support the following standard KeyGenerator algorithms with the keysizes in parentheses:
Key Employment Generators Esp
AES(128)DES(56)DESede(168)HmacSHA1HmacSHA256